
Introduction:
Are you curious about the latest advancements in materials science? Today, we're delving into an intriguing research article entitled "Catalytic Disconnection of C–O Bonds in Epoxy Resins and Composites." This cutting-edge study sheds light on the catalytic disconnection of carbon-oxygen (C–O) bonds in epoxy resins and composites, which holds the potential to revolutionize recycling processes and transform the materials industry. Let's explore the findings and their implications in detail.
Background:
Due to their exceptional mechanical strength, adhesion properties, and chemical resistance, epoxy resins and composites are widely used in various industries. However, their extensive use has also led to environmental concerns, as they can be challenging to recycle. The ability to efficiently disconnect C–O bonds within these materials is crucial for improving recycling methods and reducing waste.
Key Findings:
Using different catalysts, the researchers investigated the catalytic disconnection of C–O bonds in epoxy resins. Their findings revealed that 3 mol% of a transition metal catalyst (triphos-Ru-TMM) was optimally effective at 160 degrees Celsius, leading to the successful disconnection of the C–O bonds and the consequent depolymerization of the epoxy materials as shown in the figure below.
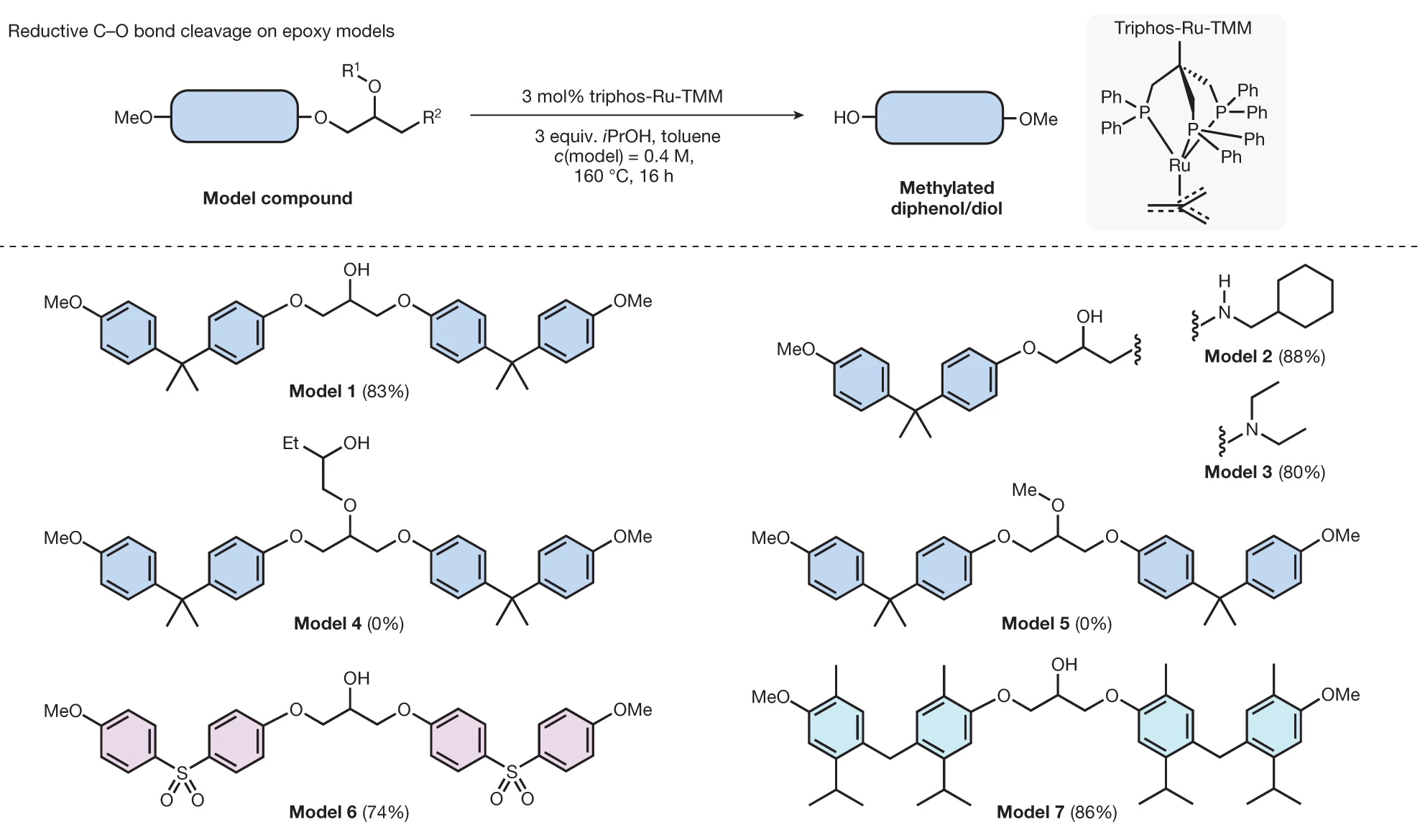

Reaction condition for the catalytic reductive cleavage of C-O bonds in epoxy resins with various structures
This groundbreaking discovery has far-reaching implications, as it enables the recycling of epoxy resins and composites at the molecular level. The ability to break down these materials into their constituent parts allows for more efficient recycling processes and paves the way for a more circular economy in the materials industry.
Implications and Future Research:
The study's findings have the potential to transform the recycling landscape for epoxy resins and composites. By understanding the mechanisms behind the catalytic disconnection of C–O bonds, we can develop more efficient and eco-friendly recycling processes for these widely used materials. This will ultimately contribute to a more sustainable future by reducing waste and conserving resources.
Furthermore, this research opens up new avenues for future investigations into the disconnection of C–O bonds in other polymer materials. By broadening our understanding of these processes, we can further optimize recycling methods and promote a more sustainable materials industry.
Conclusion:
The article "Catalytic Disconnection of C–O Bonds in Epoxy Resins and Composites" offers a fascinating insight into the complex world of materials science, revealing a novel approach to recycling epoxy materials. As our understanding of these processes continues to grow, so too does our ability to create a more sustainable future for the materials industry and the environment.